APPL 1.0
Documentation
APPL (Avasaram Platform Programming Language) is
a powerful language used to extend the built in functionalities of the Avasaram
platform. It could be used to create advanced filters and advanced
display columns. Language syntax for APPL is very similar to the
popular language JAVA.
APPL scripts must start with a curly brace ”{”
and end with a curly brace “}”. All the statements in the script must
end with a semicolon “;”.
A sample script for APPL filters to find stocks
with last traded price greater than 10.
{
stock.getLast() > 10;
}
A sample script to add an APPL display column of
maximum return probability.
{
strategy.getMaxReturnProbability();
}
APPL Core Objects and Classes
|
Object/Class
|
Description
|
|
strategy
|
The
strategy object which contains information about the strategy being accessed.
Example to get the ticker
symbol of the underlying stock.
strategy.getTicker()
|
|
stock
|
The
underlying object for the strategy.
Example to get the last
traded price.
stock.getLast()
|
|
longLegOne
|
The first
long leg associated with the strategy. In case of a married put strategy this
is the put option purchased to protect the stock. Presence of this object
depends on the strategy that is being accessed.
Example to get the option
symbol.
longLegOne.getOptionSymbol()
|
|
shortLegOne
|
The first
short leg associated with the strategy. In case of a covered call strategy
this is the call option sold against the stock. Presence of this object
depends on the strategy that is being accessed.
Example to get the option
symbol.
shortLegOne.getOptionSymbol()
|
|
longLegTwo
|
The
second long leg associated with the strategy. Presence of this object
depends on the strategy that is being accessed. This is usually present in a
multi leg strategy like butterflies and condors.
Example to get the option
symbol.
shortLegOne.getOptionSymbol()
|
|
shortLegTwo
|
The
second short leg associated with the strategy. Presence of this object
depends on the strategy that is being accessed. This is usually present in a
multi leg strategy like butterflies and condors.
Example to get the option
symbol.
shortLegOne.getOptionSymbol()
|
|
Util
|
This
is a utility class containing commonly used methods.
|
|
Math
|
Utility
class containing mathematical functions.
Example to get the square
root.
Math.sqrt(4)
|
|
TA
|
Technical
Analysis class containing TA specific functions.
Example
to
check for existence of Bullish DOJI Pattern in last 20 days
TA.hasPattern(CandleStickPattern.DOJI,
Bias.BULLISH,20);
|
Filters using APPL script
Advanced filters could be made using APPL scripts. The
APPL expression used for building the filter must evaluate to a Boolean value.
To add a new APPL filter click on the “Add APPL Filter” button from the
custom screener. See the figure below.

Figure below shows an example APPL filter which returns
strategies with Annual Return > 10
After entering the script click the validate button to
check for any error. After validation click save to add the filter to your screener.

Examples
1. Filter
to retrieve strategy data which has its stock with last traded price between 10
and 50.
{
stock.getLast()
> 10 && stock. getLast() < 50;
}
2. Filter to retrieve a stock which has an occurrence of Candle stick
pattern “Two Crows” in last 20 days.
{
TA.hasPattern(CandleStickPattern.TWO_CROWS,Bias.BEARISH,20);
}
3. Filter to find a Delta Neutral position for calendar spread.
{
shortDelta
= shortLegOne.getDelta();
longDelta
= longLegOne.getDelta();
netDelta
= longDelta - shortDelta;
netDelta
< 0.02;
}
Display Column using APPL script
Display columns could be added to the screener results
easily by creating an APPL script. Click on the “Add APPL Column” to
create a new display column. See the figure below.
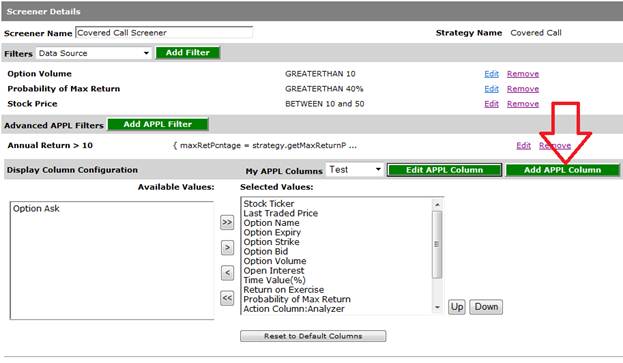
After entering the script click the “validate and
preview” button to check for any errors and preview results. After
validation click “save” to add the display column to your screener.
Unlike the filters the script for the display column does not have to evaluate
to boolean.
Figure below shows the APPL script for display column
which shows a simple annualized return.

Examples
1. APPL
Script to create a display column to create a simple annualized rate of return
for a covered call strategy.
{
maxRetPcntage
= strategy.getMaxReturnPercentage();
returnPeriod
= shortLegOne.getOptionExpiryInDays();
annualReturn
= (maxRetPcntage/returnPeriod)*365;
Math.convertToTwoDigitPrecision(annualReturn);
}
2. APPL
Script to create a display column showing Net Delta for calendar spread.
{
shortDelta
= shortLegOne.getDelta();
longDelta
= longLegOne.getDelta();
netDelta
= longDelta - shortDelta;
Math.convertToTwoDigitPrecision(netDelta);
}
|
Available methods for Object : strategy
|
|
Function Name
|
Return Type
|
Description
|
|
getTicker()
|
String
|
Gets the ticker symbol associated with the stock of this
strategy.
Example Usage:
strategy.getTicker();
|
|
getStrategyShortName()
|
String
|
Gets the short name for the strategy.
Example Usage:
strategy.getStrategyShortName();
|
|
getMaxReturnPercentage()
|
double
|
Gets the maximum return in percentage
|
|
getMaxReturn()
|
double
|
Gets the maximum return
|
|
getMaxRisk()
|
double
|
Gets the maximum risk for the strategy
|
|
getMaxReturnProbability()
|
double
|
Gets the probability of maximum return
|
|
getAnyReturnProbability()
|
double
|
Gets the probability of any return
|
|
Available methods for Object : stock
|
|
Function Name
|
Return Type
|
Description
|
|
getLast()
|
double
|
Gets
the last traded price
Example
Usage:
stock.getLast();
|
|
getOpen()
|
double
|
Gets
the opening price
Example
Usage:
stock.getOpen();
|
|
getHigh()
|
double
|
Gets
the high price
|
|
getLow()
|
double
|
Gets
the low price
|
|
getBid()
|
double
|
Gets
the bid price
|
|
getBidSize()
|
double
|
Gets
the bid size
|
|
getAsk()
|
double
|
Gets
the ask price
|
|
getAskSize()
|
double
|
Gets
the ask size
|
|
getWkLow52()
|
double
|
Gets
the 52 Week low
|
|
getWkHigh52()
|
double
|
Gets
the 52 Week High
|
|
getAvgVolume()
|
long
|
Gets
the average volume
|
|
getStockName()
|
String
|
Gets
the Name of the stock
|
|
getVolumeTraded()
|
long
|
Gets
the volume traded
|
|
getAtmCallVolatility()
|
double
|
Get
the At the Money Volatility of the Call Options
|
|
getAtmPutVolatility()
|
double
|
Get
the At the Money Volatility of the Put Options
|
|
Available methods for Objects : longLegOne/longLegTwo/shortLegOne/shortLegTwo
|
|
Function Name
|
Return Type
|
Description
|
|
getExpiry()
|
String
|
Gets
the expiry of the option as a String
Example
Usage:
longLegOne.getExpiry();
OR
longLegTwo.getExpiry();
OR
shortLegOne.getExpiry();
OR
shortLegTwo.getExpiry();
|
|
getOptionExpiryInDays()
|
long
|
Gets
the expiry of the option in days
|
|
getOptionSymbol()
|
String
|
Gets
the option symbol
|
|
getOptionType()
|
String
|
Gets
the type of Option. ”C” for Call and “P” for Put
|
|
isITM()
|
boolean
|
Returns
true if the option is in the money
|
|
getImpliedVolatility()
|
double
|
Gets
the implied volatility for the option
|
|
getStrike()
|
double
|
Gets
the Strike of this option
|
|
getBid()
|
double
|
Gets
the bid price for the option.
|
|
getAsk()
|
double
|
Gets
the ask price for the option
|
|
getLast()
|
double
|
Gets
the last traded price for the option.
|
|
getVolume()
|
long
|
Gets
the trade volume for the option.
|
|
getOpenInterest()
|
long
|
Gets
the open interest for the option.
|
|
getDelta()
|
double
|
Gets
the delta for the option.
|
|
getGamma()
|
double
|
Gets
the gamma for the option
|
|
getTheta()
|
double
|
Gets
the theta for the option.
|
|
getVega()
|
double
|
Gets
the vega for the option.
|
|
getRho()
|
double
|
Gets
the rho for the option.
|
|
Available methods for Class : Math
|
|
Function Name
|
Return Type
|
Description
|
|
abs(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the absolute value of a double
value.
Example Usage:
Math.abs(12);
|
|
acos(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the arc cosine of a value; the returned angle is in the
range 0.0 through pi
Example Usage:
Math.acos(12);
|
|
asin(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the arc sine of a value; the returned angle is in the
range -pi/2 through pi/2.
|
|
atan(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the arc tangent of a value; the returned angle is in the
range -pi/2 through pi/2.
|
|
cbrt(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the cube root of a double value
|
|
ceil(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the smallest (closest to negative infinity) double value
that is greater than or equal to the argument and is equal to a mathematical
integer.
|
|
cos(double
a)
|
double
|
returns the trigonometric cosine of an angle.
|
|
cosh(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a double
value.
|
|
exp(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns Euler's number e raised to the power of a double
value.
|
|
log(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the natural logarithm (base e) of a double
value.
|
|
log10(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the base 10 logarithm of a double value
|
|
pow(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the value of the first argument raised to the power of
the second argument.
|
|
sin(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the trigonometric sine of an angle.
|
|
sqrt(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the correctly rounded positive square root of a double value
|
|
tan(double
a)
|
double
|
Returns the trigonometric tangent of an angle.
|
|
convertToTwoDigitPrecision(double
a)
|
double
|
Converts
the number to have a two digit precision after the decimal
|
|
convertToThreeDigitPrecision(double
a)
|
double
|
Converts the number to have a three digit precision after the decimal
|
|
Available methods for Class : TA
|
|
Function Name
|
Return Type
|
Description
|
|
hasPattern(
CandleStickPattern.type,
Bias.type,
int noOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Check
for the existence of the CandleStick pattern with the Bias (Bullish,Bearish)
in the specified days.
Example
Usage:
TA.hasPattern(CandleStickPattern.DOJI,
Bias.BULLISH,20);
See
below for the complete list of CandleStick Pattern types
|
|
hasPositiveSMACrossover(
int lineOnePeriod,
int lineTwoPeriod,
int days
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if SMA line-1 Crossed SMA line-2 towards positive (Upward) direction.
|
|
hasNegativeSMACrossover(
int lineOnePeriod,
int lineTwoPeriod,
int days
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if SMA line-1 Crossed SMA line-2 towards negative (Downward) direction.
|
|
hasSMAAboveStock(
int period,
int noOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if SMA line is above the stock line in the specified days.
|
|
hasSMABelowStock(
int period,
int noOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if SMA line is below the stock line in the specified days.
|
|
hasPositiveEMACrossover(
int lineOnePeriod,
int lineTwoPeriod,
int days
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if EMA line-1 Crossed EMA line-2 towards positive (Upward) direction.
|
|
hasNegativeEMACrossover(
int lineOnePeriod,
int lineTwoPeriod,
int days
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if EMA line-1 Crossed EMA line-2 towards negative (Downward) direction.
|
|
hasEMAAboveStock(
int period,
int noOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if EMA line is above the stock line in the specified days.
|
|
hasEMABelowStock(
int period,
int noOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if EMA line is below the stock line in the specified days.
|
|
hasWillamsRCrossAbove(
int period,
double value,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if WillamsR line with period “period” crossed above the value in the
specified days.
|
|
hasWillamsRCrossBelow(
int period,
double value,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if WillamsR line with period “period” crossed below the value in the
specified days.
|
|
hasWillamsRAbove(
int period,
double value,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if WillamsR line with period “period” is above the value in the specified
days.
|
|
hasWillamsRBelow(
int period,
double value,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if WillamsR line with period “period” is below the value in the specified
days.
|
|
hasRSICrossAbove(
int period,
double value,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if RSI line with period “period” crossed above the value in the specified
days.
|
|
hasRSICrossBelow(
int period,
double value,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if RSI line with period “period” crossed below the value in the specified
days.
|
|
hasRSIAbove(
int period,
double value,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if RSI line with period “period” is above the value in the specified days.
|
|
hasRSIBelow(
int period,
double value,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if RSI line with period “period” is below the value in the specified days.
|
|
hasMFICrossAbove(
int period,
double value,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if MFI line with period “period” crossed above the value in the specified
days.
|
|
hasMFICrossBelow(
int period,
double value,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if MFI line with period “period” crossed below the value in the specified
days.
|
|
hasMFIAbove(
int period,
double value,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if MFI line with period “period” is above the value in the specified days.
|
|
hasMFIBelow(
int period,
double value,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if MFI line with period “period” is below the value in the specified days.
|
|
hasMACDAboveSignal(
int fastPeriod,
int slowPeriod,
int signalPeriod,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if MACD Crossed above the signal line in the specified days.
|
|
hasMACDBelowSignal(
int fastPeriod,
int slowPeriod,
int signalPeriod,
int lastNoOfDays)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if MACD Crossed below the signal line in the specified days.
|
|
hasTouchedUpperBBand(
int period,
int deviation,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if the underlying’s Closing price touched the Upper Bollinger Band in the
specified days.
|
|
hasTouchedLowerBBand(
int period,
int deviation,
int lastNoOfDays
)
|
boolean
|
Checks
if the underlying’s Closing price touched the Lower Bollinger Band in the
specified days.
|
|
probabilityStockCrossAbove(
double price,
int nofDays
)
|
double
|
Returns
the probability of stock crossing above the price at the specified number of
days.
|
|
probabilityStockCrossBelow(
double price,
int nofDays
)
|
double
|
Returns
the probability of stock crossing below the price at the specified number of
days.
|
|
probabilityStockTouch(
double priceOne,
int nofDays
)
|
double
|
Returns
the probability of stock touching the price in specified number of days.
|
|
probabilityStockBetween(
double priceOne,
double priceTwo,
int nofDays
)
|
double
|
Returns
the probability of stock being in the range at the specified number of days.
|
|
probabilityStockCrossAbove(
double price,
double volatility,
int nofDays
)
|
double
|
Returns
the probability of stock crossing above the price at the specified number of days.
|
|
probabilityStockCrossBelow(
double price,
double volatility,
int nofDays
)
|
double
|
Returns
the probability of stock crossing below the price at the specified number of
days.
|
|
probabilityStockTouch(
double priceOne,
double volatility,
int nofDays
)
|
double
|
Returns
the probability of stock touching the price in specified number of days.
|
|
probabilityStockBetween(
double priceOne,
double priceTwo,
double volatility,
int nofDays
)
|
double
|
Returns
the probability of stock being in the range at the specified number of days.
|
|
|
|
|
|
CandleStick Pattern Types
|
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
TWO_CROWS
|
Two
Crows Pattern.
Example
Usage:
CandleStickPattern.TWO_CROWS
|
|
THREE_BLACK_CROWS
|
Three
Black Crows Pattern
|
|
THREE_INSIDE_UP_DOWN
|
Three
Inside Up/Down Pattern
|
|
THREE_LINE_STRIKE
|
Three
Line Strike Pattern
|
|
THREE_OUTSIDE
|
Three
Outside Up/Down Pattern
|
|
THREE_STARS_IN_SOUTH
|
Three
Stars In The South Pattern
|
|
THREE_WHITE_SOLDIERS
|
Three
Advancing White Soldiers Pattern
|
|
ABANDONED_BABY
|
Abandoned
Baby Pattern
|
|
ADVANCE_BLOCK
|
Advance
Block Pattern
|
|
BELT_HOLD
|
Belt
Hold Pattern
|
|
BREAKAWAY
|
Breakaway
Pattern
|
|
CLOSING_MARUBOZU
|
Closing
Marubozu Pattern
|
|
CONCEAL_BABY_SWALL
|
Concealing
Baby Swallow Pattern
|
|
COUNTERATTACK
|
Counterattack
Pattern
|
|
DARK_CLOUD_COVER
|
Dark
Cloud Cover Pattern
|
|
DOJI
|
Doji
Pattern
|
|
DOJI_STAR
|
Doji
Star Pattern
|
|
DRAGONFLY_DOJI
|
Dragon
Fly Doji Pattern
|
|
ENGULFING
|
Engulfing
Pattern
|
|
EVENING_DOJI_STAR
|
Evening
Doji Star Pattern
|
|
EVENING_STAR
|
Evening
Star Pattern
|
|
GAP_SIDE_SIDE_WHITE
|
Up/Down
Gap Side-By-Side White Lines
|
|
GRAVE_STONE_DOJI
|
Gravestone
Doji
|
|
HAMMER
|
Hammer
Pattern
|
|
HANGINGMAN
|
Hanging
Man Pattern
|
|
HARAMI
|
Harami
Pattern
|
|
HARAMICROSS
|
Harami
Cross Pattern
|
|
HIGHWAVE
|
High
Wave Pattern
|
|
HIKKAKE
|
Hikkake
Pattern
|
|
HIKKAKEMOD
|
Hikkake
Modified Pattern
|
|
HOMING_PIGEON
|
Homing
Pegion Pattern
|
|
IDENTICAL_THREE_CROWS
|
Identical
Three Crows Pattern
|
|
INNECK
|
In
Neck Pattern
|
|
INVERTED_HAMMER
|
Inverted
Hammer Pattern
|
|
KICKING
|
Kicking
Pattern
|
|
KICKING_BY_LENGTH
|
Kicking
- bull/bear determined by the longer marubozu Pattern
|
|
LADDERBOTTOM
|
Ladder
Bottom Pattern
|
|
LONGLEGGED_DOJI
|
Long
Legged Doji Pattern
|
|
LONGLINE
|
Long
line Pattern
|
|
MARUBOZU
|
Marubozu
Pattern
|
|
MATCHING_LOW
|
Matching
Low Pattern
|
|
MATHOLD
|
Mat
Hold Pattern
|
|
MORNING_DOJI_STAR
|
Morning
Doji Star Pattern
|
|
MORNINGSTAR
|
Morning
Star Pattern
|
|
ONNECK
|
On
Neck Pattern
|
|
PIERCING
|
Piercing
Pattern
|
|
RICKSHAW_MAN
|
Rickshaw
Man Pattern
|
|
RISEFALL_THREE_METHODS
|
Rising/Falling
Three Methods Pattern
|
|
SEPARATING_LINES
|
Separating
Lines Pattern
|
|
SHOOTING_STAR
|
Shooting
Star Pattern
|
|
SHORTLINE
|
Short
Line Pattern
|
|
SPINNING_TOP
|
Spinning
Top Pattern
|
|
STALLED_PATTERN
|
Stalled
Pattern Pattern
|
|
STICKSANDWICH
|
Stick
Sandwich Pattern
|
|
TAKURI
|
Takuri
Pattern
|
|
TASUKIGAP
|
Tasuki
Gap Pattern
|
|
THRUSTING
|
Thrusting
Pattern
|
|
TRISTAR
|
Tristar
Pattern
|
|
UNIQUE_THREE_RIVER
|
Unique
Three River Pattern
|
|
UPSIDEGAP_TWO_CROWS
|
Upside
Gap Two Crows Pattern
|
|
XSIDEGAP3METHODS
|
Upside/Downside
Gap Three Methods
|
|
Bias Types
|
|
BULLISH
|
Bullish
Direction
Usage:
Bias.BULLISH
Example
hasPattern(CandleStickPattern.DOJI, Bias.BULLISH,20);
|
|
BEARISH
|
Bearish
Direction
|
|
NEUTRAL
|
Neutral
Direction
|
APL Language Elements
|
Item
|
Description
|
|
Comments
|
Also specified using //, e.g.
//
This is a comment
Multiple lines comments are specified using /*...*/, e.g.
/*
This is a
multi-line comment */
|
|
Identifiers / variables
|
Must start with a-z, A-Z. Can
then be followed by 0-9, a-z, A-Z, _ or $. e.g.
- Valid: var1,a99
- Invalid: 9v,!a99,1$
Variable names are case-sensitive,
e.g. var1 and Var1 are different variables.
N.B. the
following keywords are reserved, and cannot be used as a variable name or
property when using the dot operator:
or, and, eq, ne, lt, gt, le,
ge, div, mod, not, null, true, false, new.
|
|
Scripts
|
A script in APL is made up of zero or more statements.
|
|
Statements
|
A statement can be the empty statement, the semicolon (;) ,
block, assignment or an expression. Statements are optionally terminated with
a semicolon.
|
|
Block
|
A block is simply multiple statements inside curly braces ({, }).
|
|
Assignment
|
Assigns the value of a variable (var =
'a value')
|
|
Method calls
|
Calls a method of an object, e.g.
Math.sqrt(4)
will call the sqrt method from Math
object.
|
Literals
|
Item
|
Description
|
|
Integer Literals
|
1 or more digits from 0 to 9
|
|
Floating point Literals
|
1 or more digits from 0 to 9,
followed by a decimal point and then one or more digits from 0 to 9.
|
|
String literals
|
Can start and end with "
delimiters, e.g.
"Hello
world"
The
escape character is \; it only escapes the string delimiter
|
|
Boolean literals
|
The literals true and false can
be used, e.g.
val1
== true
|
|
Null literal
|
The null value is represented as in java using the literal null, e.g.
val1 == null
|
|
Array literal
|
A [ followed by one or more expressions separated by , and
ending with ], e.g.
[ 1,
2, "three" ]
This syntax creates an Object[].
APPL will attempt to strongly
type the array; if all entries are of the same class or if all entries are
Number instance, the array literal will be an MyClass[] in
the former case, a Number[] in the latter case.
Furthermore, if all entries
in the array literal are of the same class and that class has an equivalent
primitive type, the array returned will be a primitive array. e.g. [1, 2,
3] will be interpreted as int[].
|
Operators
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
Boolean and
|
The usual && operator can be used, e.g.
cond1
&& cond2
|
|
Boolean or
|
The usual || operator can be used
cond1
|| cond2
|
|
Boolean not
|
The usual ! operator can be used e.g.
!cond1
|
|
Bitwise and
|
The usual & operator is used, e.g.
33
& 4
, 0010 0001 & 0000 0100 = 0.
|
|
Bitwise or
|
The usual | operator is used, e.g.
33 | 4
, 0010 0001 | 0000 0100 = 0010 0101 = 37.
|
|
Bitwise xor
|
The usual ^ operator is used, e.g.
33 ^ 4
, 0010 0001 ^ 0000 0100 = 0010 0100 = 37.
|
|
Bitwise complement
|
The usual ~ operator is used, e.g.
~33
, ~0010 0001 = 1101 1110 = -34.
|
|
Ternary conditional ?:
|
The usual ternary conditional operator condition
? if_true : if_false operator can be used ,e.g.
val1 ?
val1 : val2
|
|
Equality
|
The usual == operator can be used. For example
val1
== val2
1. null is
only ever equal to null, that is if you compare null to any non-null value,
the result is false.
2. Equality
uses the java equals method
|
|
Inequality
|
The usual != operator can be. For example
val1
!= val2.
|
|
Less Than
|
The usual < operator can be used .For example
val1
< val2
|
|
Less Than Or Equal To
|
The usual <= operator can be used. For example
val1
<= val2
|
|
Greater Than
|
The usual > operator can be used as well as the abbreviation gt. For
example
val1
> val2
|
|
Greater Than Or Equal To
|
The usual >= operator can be used. For example
val1
>= val2
|
|
Addition
|
The usual + operator is used. For example
val1 +
val2
|
|
Subtraction
|
The usual - operator is used. For example
val1 -
val2
|
|
Multiplication
|
The usual * operator is used. For example
val1 *
val2
|
|
Division
|
The usual / operator is used. For example
val1 /
val2
|
|
Modulus (or remainder)
|
The % operator is used
5 % 2
|
|
Negation
|
The unary - operator is used. For example
-12
|
|
Array access
|
Array elements may be accessed using square brackets e.g.
arr1[0]
|
Conditionals
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
if
|
Classic, if/else statement, e.g.
if ((x * 2) ==
5) {
y = 1;
} else {
y = 2;
}
|
|
|





 Contact
Contact